
What is a hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI)?
Imagine if you could combine your computer’s storage, memory, and processing power into one simple box that does everything—no messy wires, no juggling between different parts. That’s basically what hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) does, but on a much bigger scale for companies.
Instead of having separate servers, storage systems, and networking gear, HCI puts everything into a single, software-driven system. It’s like turning a bunch of separate tools into one smart, all-in-one machine. This makes it easier to manage, faster to scale, and often cheaper to run. It's a modern way to keep things simple and efficient in data centers.
Benefits of HCI:
Simplified Management: By consolidating resources into a single platform, HCI reduces the need for separate management tools and interfaces, making it easier for IT teams to oversee operations.
Scalability: Organizations can easily scale their infrastructure by adding more nodes to the HCI system, allowing them to grow their IT capabilities in line with business needs.
Cost Efficiency: HCI reduces the need for separate hardware components, lowering capital and operational expenses.
Improved Performance: With integrated resources, HCI can optimize performance by reducing latency and improving data access speeds.
Difference between HCI & Hypervisor
A hypervisor is like a smart software layer that lets you run multiple virtual computers—called virtual machines (VMs)—on a single physical computer. Each VM acts like a real computer, with its own operating system (Windows, Linux, etc.) and applications, but they all share the same physical hardware. The hypervisor manages how much CPU, memory, storage, and other resources each VM gets, and keeps them all running smoothly and securely.
This is what makes virtualization possible—helping businesses do more with less hardware, reduce costs, and improve flexibility.
Types of Hypervisors:
There are two main types of hypervisors:
1. Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare Metal)
This type runs directly on the physical hardware, without needing an operating system underneath. It’s super efficient and often used in enterprise data centers.
- Examples: VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, KVM
- Use case: Best for performance, security, and scalability—used in large-scale environments.
2. Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted)
This type runs on top of an existing operating system like Windows or macOS. It’s easier to set up and great for testing or development.
- Examples: VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, Parallels
- Use case: Ideal for personal use, developers, or running multiple OSes on a laptop.
Neverinstall's HCI - Native Virtualization
Neverinstall's HCI is a cloud-native solution that leverages Kubernetes for orchestration and management. It harnesses the capabilities of a KVM hypervisor alongside advanced proprietary virtualization tools, Ceph distributed storage, and the flexibility of Docker containers. Neverinstall's HCI is designed to run on commodity hardware, allowing organizations to build scalable and cost-effective virtualized environments. The platform's Kubernetes-based architecture enables seamless deployment and management of virtual machines centrally.
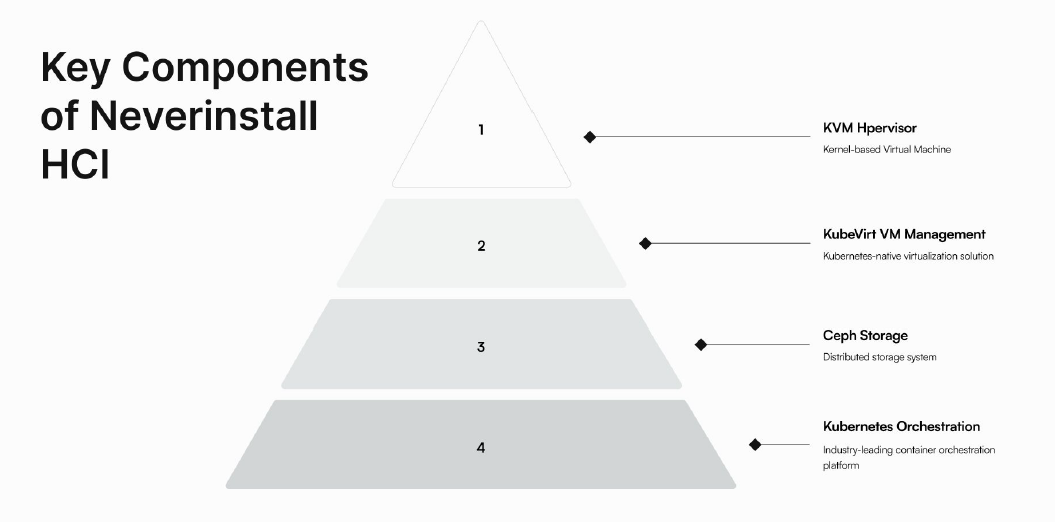
Key Components
- KVM Hypervisor: A robust, widely-used open-source hypervisor forming the foundation for virtual machine deployment within Neverinstall HCI.
- KubeVirt: A Kubernetes-native virtualization solution that manages the lifecycle of virtual machines within a Kubernetes cluster.
- Ceph Storage: A distributed storage system ensuring high availability and reliability for virtual machine storage.
- Kubernetes Orchestration: Industry-leading orchestration automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications and virtual machines.
By transforming virtual machines into Docker containers, Neverinstall HCI not only overcomes the limitations of traditional hypervisors but also sets a new benchmark for efficiency, scalability, and security in virtualization technology.
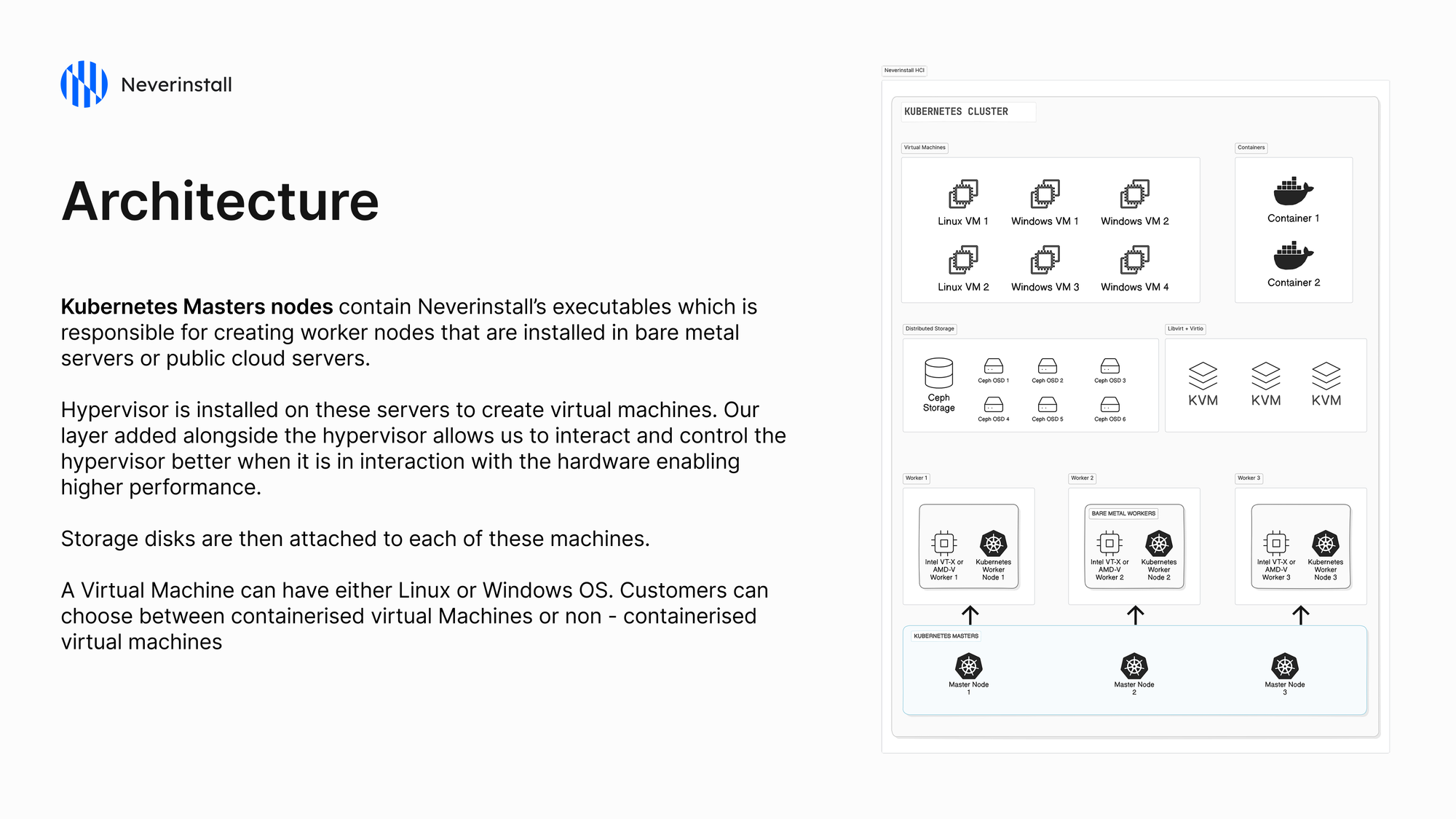
In the architecture of Neverinstall HCI, the Kubernetes Master nodes play a crucial role by containing the executables responsible for creating worker nodes. These worker nodes can be installed on either bare metal servers or public cloud servers.
A hypervisor is installed on these servers to facilitate the creation of virtual machines. The layer added by Neverinstall alongside the hypervisor allows enhanced interaction and control over the hypervisor, enabling higher performance by optimizing its interaction with the underlying hardware.
Once the hypervisor is operational, storage disks are attached to each of these machines, providing the necessary storage resources for the virtual machines.
Customers have the flexibility to choose between containerized virtual machines and non-containerized virtual machines, with support for both Linux and Windows operating systems. This versatility allows organizations to tailor their virtualized environments to meet specific needs and preferences.
Neverinstall's Hypervisor - Built on KVM
The Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is an open-source hypervisor integrated into the Linux kernel, providing full virtualization capabilities. KVM allows each virtual machine to function as a separate physical machine, complete with virtualized hardware such as CPUs, memory, storage, and network cards. Its integration with Linux ensures high performance and security, benefiting from regular updates and enhancements of the Linux kernel.
Advantages of KVM
- Performance: KVM leverages hardware virtualization extensions (Intel VT-x and AMD-V) to deliver near-native performance for virtual machines.
- Isolation: Each VM is isolated from the others, enhancing security and stability.
- Cost-Effective: Being open-source, KVM is free to use, reducing overall costs compared to proprietary hypervisors like VMware.
- Flexibility: Supports a wide range of guest operating systems, including various Linux distributions and Windows.
KubeVirt VM Management
KubeVirt extends Kubernetes by adding the ability to manage virtual machines alongside containerized workloads. This integration provides a unified platform for both types of workloads, enabling organisations to use familiar Kubernetes tools and workflows for VM management. KubeVirt simplifies the lifecycle management of virtual machines, making it easier to deploy, scale, and manage VMs in a Kubernetes environment.
Ceph Storage
Ceph is a scalable, open-source storage solution that provides distributed storage capabilities. It supports object, block, and file storage, ensuring high availability and reliability for virtual machine storage. Ceph's architecture eliminates single points of failure, making it an ideal choice for enterprise-level storage needs.
Kubernetes Orchestration
Kubernetes is the industry-standard platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Within Neverinstall HCI, Kubernetes orchestrates both containerized applications and virtual machines, ensuring optimal resource utilisation and dynamic workload management. This orchestration capability allows Neverinstall HCI to provide a scalable and efficient infrastructure management solution.
Advantages of Integrated Components
The combination of KVM, KubeVirt, Ceph, and Kubernetes ensures superior performance, scalability, and flexibility, setting a new standard in the virtualization landscape.
Key Benefits
- High Performance
- Enhanced Scalability
- Robust Reliability
- Unified Management & Isolation
Neverinstall HCI represents a significant leap forward in virtualization technology, providing businesses with a flexible tool to enhance their IT infrastructure, without any of the usual hurdles.
Product Comparison: Neverinstall HCI vs. Leading Hypervisors
To provide a clear and concise comparison of Neverinstall HCI with other leading hypervisors like VMware vSphere, Proxmox VE, and Citrix Xen, we will focus on key aspects such as performance, cost, ease of management, and scalability.
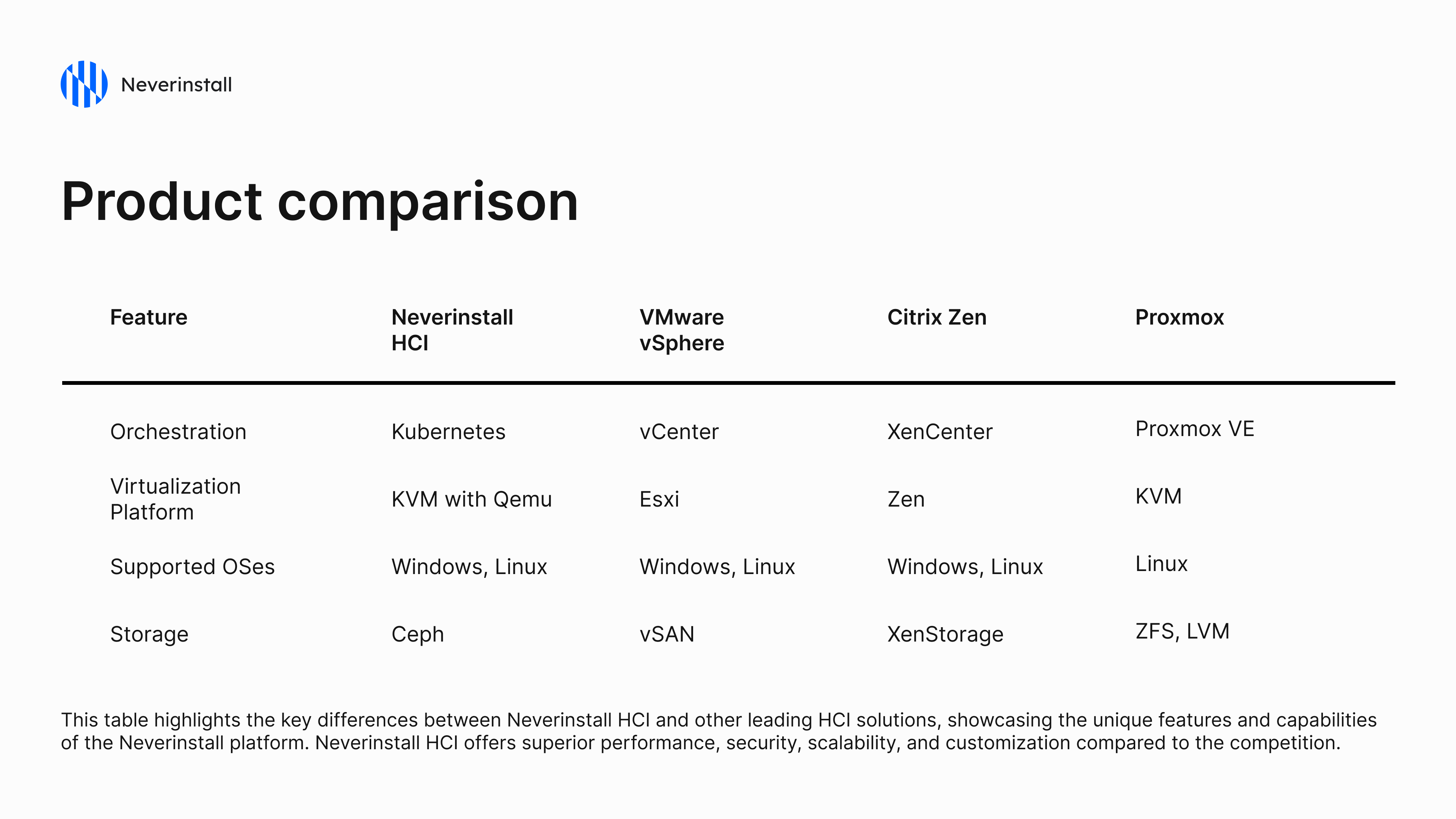
In summary,
Neverinstall HCI places a strong emphasis on security, leveraging the inherent security features of Docker containers and Kubernetes. Virtual machines packaged as Docker containers benefit from the isolation and resource constraints provided by the container runtime, reducing the attack surface and potential vulnerabilities. Additionally, Kubernetes' built-in security mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and network policies, ensure that the virtual machines and the underlying infrastructure are protected from unauthorized access and threats.



Join the conversation.